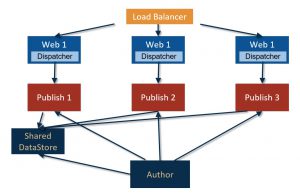
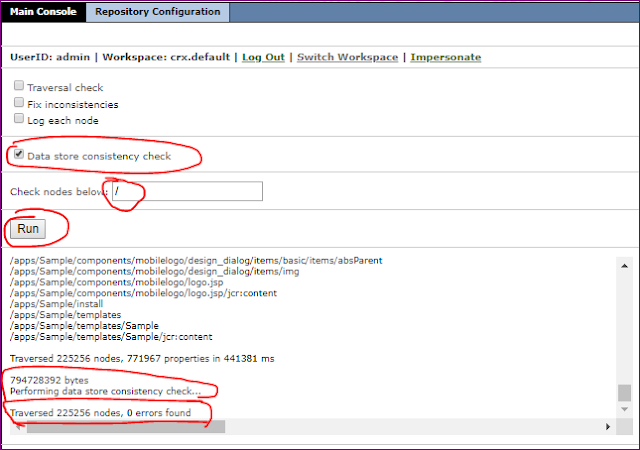
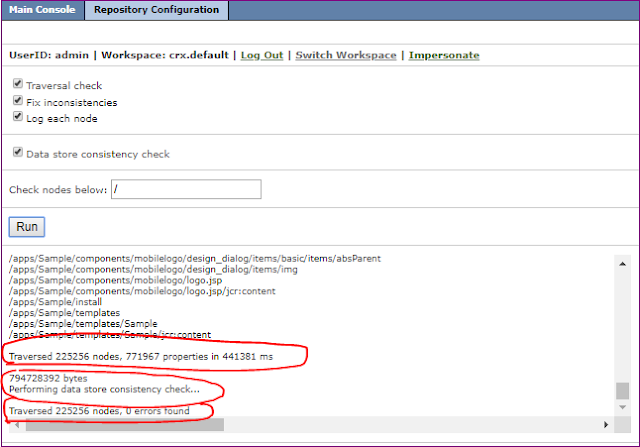
In Adobe Experience Manager (AEM), binary data can be stored independently from the content nodes. The binary data is stored in a data store, whereas content nodes are stored in a node store.
Both data stores and node stores can be configured using OSGi configuration. Each OSGi configuration is referenced using a persistent identifier (PID).
Node Store
Currently, there are two storage implementations available in AEM6: Tar Storage and MongoDB Storage.
Configure the node store by creating a configuration file with the name of the node store option you want to use in the crx-quickstart/install
segment node store
document node store
segment node store
The segment node store is the basis of Adobe’s TarMK implementation in AEM6. It uses the org.apache.jackrabbit.oak.segment.SegmentNodeStoreService PID for configuration.
You can configure the following options:
repository.home: Path to repository home under which repository-related data is stored. By default, segment files are stored under the crx-quickstart/segmentstore directory.
tarmk.size: Maximum size of a segment in MB. The default maximum is 256MB.
customBlobStore: Boolean value indicating that a custom data store is used. The default value is false.
The Tar storage uses tar files. It stores the content as various types of records within larger segments. Journals are used to track the latest state of the repository.
There are several key design principles it was build around:
Immutable Segments
The content is stored in segments that can be up to 256KiB in size. They are immutable, which makes it easy to cache frequently accessed segments and reduce system errors that may corrupt the repository.
Each segment is identified by a unique identifier (UUID) and contains a continuous subset of the content tree. In addition, segments can reference other content. Each segment keeps a list of UUIDs of other referenced segments.
Locality
Related records like a node and its immediate children are usually stored in the same segment. This makes searching the repository very fast and avoids most cache misses for typical clients that access more than one related node per session.
Compactness
The formatting of records is optimized for size to reduce IO costs and to fit as much content in caches as possible.
document node store
The document node store is the basis of AEM’s MongoMK implementation. It uses the org.apache.jackrabbit.oak.plugins.document.DocumentNodeStoreService PID.
The following configuration options are available:
mongouri: The MongoURI required to connect to Mongo Database. The default is mongodb://localhost:27017
db: Name of the Mongo database. The default is Oak. However, new AEM 6 installations use aem-author as the default database name.
cache: The cache size in MB. This is distributed among various caches used in DocumentNodeStore. The default is 256
changesSize: Size in MB of capped collection used in Mongo for caching the diff output. The default is 256
customBlobStore: Boolean value indicating that a custom data store will be used. The default is false.
The MongoDB storage leverages MongoDB for sharding and clustering. The repository tree is kept in one MongoDB database where each node is a separate document.
It has several particularities:
Revisions
For each update (commit) of the content, a new revision is created. A revision is basically a string that consists of three elements:
A timestamp derived from the system time of the machine it was generated on
A counter to distinguish revisions created with the same timestamp
The cluster node id where the revision was created
Branches
Branches are supported, which allows client to stage multiple changes and make them visible with a single merge call.
Previous documents
MongoDB storage adds data to a document with every modification. However, it only deletes data if a cleanup is explicitly triggered. Old data is moved when a certain threshold is met. Previous documents only contain immutable data, which means they only contain committed and merged revisions.
Cluster node metadata
Data about active and inactive cluster nodes is kept in the database in order to facilitate cluster operations.
When to use MongoDB with AEM
MongoDB will typically be used for supporting AEM author deployments where one of the following criteria is met:
More than 1000 unique users per day;
More than 100 concurrent users;
High volumes of page edits;
Large rollouts or activations.
The criteria above are only for the author instances and not for any publish instances which should all be TarMK based. The number of users refers to authenticated users, as author instances do not allow unauthenticated access.
If the criteria are not met, then a TarMK active/standby deployment is recommended to address availability. Generally, MongoDB should be considered in situations where the scaling requirements are more than what can be achieved with a single item of hardware.
Data Store
FileDataStore
Amazon’s Simple Storage Service (S3)
Microsoft’s Azure storage service
FileDataStore
FileDataStore present in Jackrabbit 2. It provides a way to store the binary data as normal files on the file system. It uses the org.apache.jackrabbit.oak.plugins.blob.datastore.FileDataStore PID.
These configuration options are available:
repository.home: Path to repository home under which various repository related data is stored. By default, binary files would be stored under crx-quickstart/repository/datastore directory
path: Path to the directory under which the files would be stored. If specified then it takes precedence over repository.home value
minRecordLength: The minimum size in bytes of a file stored in the data store. Binary content less than this value would be inlined.
Amazon’s Simple Storage Service (S3)
AEM can be configured to store data in Amazon’s Simple Storage Service (S3). It uses the org.apache.jackrabbit.oak.plugins.blob.datastore.S3DataStore.config PID for configuration.
Microsoft’s Azure storage service
AEM can be configured to store data in Microsoft’s Azure storage service. It uses the org.apache.jackrabbit.oak.plugins.blob.datastore.AzureDataStore.config PID for configuration.
Quick Notes:
Binary Data(Data Store) + Content Nodes(Node Store) = TAR Implementation
Node Store -> Segment Store(TAR)
By Default AEM will store in Segment Store located at crx-quickstart\repository\segmentstore. If we need to make the default path and configurations then need to add the config file in install faolder before installation
Node Store -> Document Store(MongoDB).
every commit will create a version in mongo db
Data Store -> FileData Store(FileSystem).
Data Store -> S3(Cloud).
Data Store -> Azure(Cloud).