So we will start from the basics and will touch each and every concept in detail.
Design Goals of Sling Models
- Entirely annotation-driven. "Pure" POJOs.
- Use standard annotations where possible.
- Pluggable
- OOTB, support resource properties (via ValueMap), SlingBindings, OSGi services, request attributes
- Adapt multiple objects - minimal required Resource and SlingHttpServletRequest
- The client doesn't know/care that these objects are different than any other adapter factory
- Support both classes and interfaces.
- Work with existing Sling infrastructure (i.e. not require changes to other bundles).
1. Add maven dependency to the pom.xml. If you are working with AEM 6.3, Make sure you are using the recent sling model version (1.3.2)
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.sling</groupId>
<artifactId>org.apache.sling.models.api</artifactId>
<version>1.3.2</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
2. Create a package under which you will be writing all sling models and make an entry of that package (here com.sling.models.core.models) in bundle(core) ‘s pom.xml in Sling-Model-Packages tag within maven-bundle-plugin.
Here:
<plugin>
</dependency>
2. Create a package under which you will be writing all sling models and make an entry of that package (here com.sling.models.core.models) in bundle(core) ‘s pom.xml in Sling-Model-Packages tag within maven-bundle-plugin.
Here:
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.felix</groupId>
Note: Here it is mandatory to use the object name “currentPage”. If there is a need to change the name of the page object(currentPage), the “name” attribute can help us to do so.
The sightly script to call a sling model is:
<div data-sly-use.example="com.sling.models.core.models.TestModel">
${example.pagePath}<br/>
</div>
2. ChildResource: This injector is adaptable to resource and is used to get the specific child of a resource.
The attributes of the ChildResource are:
@Model(adaptables = Resource.class)
public class TestModel {
// Injects the child of the resource using ChildResource annotation
@ChildResource(name="content")
Resource child;
public String getChildPath() {
return child.getPath();
}
}
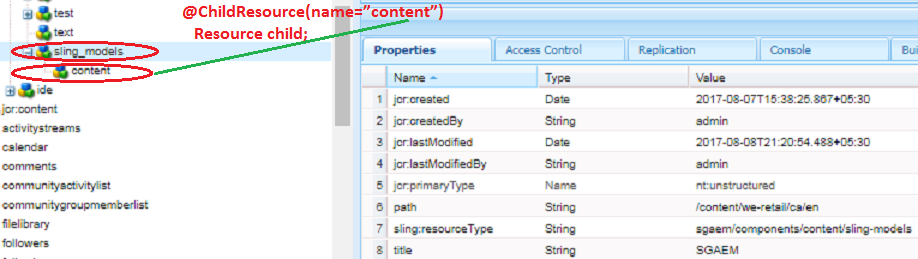
Fig - Inject Child resource directly
ChildResource annotations with its attributes:
@Model(adaptables = SlingHttpServletRequest.class)
public class TestModel {
// Injects the child of the resource using ChildResource annotation
@ChildResource(name="content",injectionStrategy= InjectionStrategy.OPTIONAL,via = "resource")
Resource child;
public String getChildPath() {
return child.getPath();
}
}
Note: ChildResource is adaptable to resource, but in the above sample, adaptables is a request. So "via" attribute is used to tell the property that the property is supposed to be fetched via resource.
3.ValueMapValue: This injector is adaptable to the resource. Through this injector, the properties of the resource can be directly injected in the sling models.
The attributes of the ValueMapValue is:
public class TestModel {
// Injects Resource and get ValueMap from the resource
@SlingObject
Resource resource;
public String getTitle() {
ValueMap valueMap = resource.adaptTo(ValueMap.class);
return valueMap.get(“title”, String.class);
}
}
In place of adapting valueMap from the resource and getting the title from valueMap, we can directly use ValueMapValue annotation in sling models.
@Model(adaptables = Resource.class)
public class TestModel {
// Injects title from ValuMapValue
@ValueMapValue
String title;
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
}

Fig - Value Map Sample
The ValueMapValue annotation using its attributes:
@Model(adaptables = SlingHttpServletRequest.class)
public class Test {
// Injects title from ValuMap annotation using its attributes
@ValueMapValue(name = "title",via = "resource",injectionStrategy = InjectionStrategy.REQUIRED)
String pageTitle;
public String getTitle() {
return pageTitle;
}
}
4.ResourcePath: ➤ If a resource is having a property whose value is a path, you can directly use that property as a resource.
➤ You can directly inject a path as a resource using this annotation.
The attributes of the ResourcePath annotation is:
public class TestModel {
//directly inject a path as a resource
@ResourcePath(path = ”/etc/social”)
Resource pathResource;
@ResourcePath(name = "path")
Resource resourcePath;
@ResourcePath(paths = {"/etc/social","/etc/tags"})
Resource[] paths;
}

Fig - Get the Resource bypassing the path dynamically in sling model
5. OSGiService: If we need to inject OSGiService in Sling Models, we can use it like this:
@Model(adaptables = Resource.class)
public class TestModel {
@OSGiService
SlingSettings slingSetttings;
}
6. SlingObject: Supports sling based Objects like request, response, ResourceResolver, Resource, and Sling ScriptHelper.
@Model(adaptables = SlingHttpServletRequest.class)
public class TestModel {
@SlingObject
Resource resource;
@SlingObject
ResourceResolver resourceResolver;
}
7.Self:
➤ Injects the adaptable object itself.
➤ An object that can be adapted from it if the self annotation is present.
The only attribute in the Self annotation is injectionStrategy.
@Model(adaptables = SlingHttpServletRequest.class)
public class SelfExampleModel {
@Self
Node node;
public String getNodePath() throws RepositoryException {
return node.getPath();
}
}
8. Request Attributes: When there are input parameters while initializing the sling model, and you want to get these parameters in the sling model, you can use this annotation.
The attributes of RequestAttribute annotation are:
public class TestModel {
//Injects all the input parameters from sightly injects as RequestAttribute in Sling Models
@RequestAttribute(name = "color")
String param;
public String getParam() {
return param;
}
}
The sightly script calls the sling Model using input parameter :
<div data-sly-use.example="${'com.sling.models.core.models.TestModel ’ @ color='red'}">
${example.param}<br/>
</div>
<artifactId>maven-bundle-plugin</artifactId>
<extensions>true</extensions>
<configuration>
<instructions>
<Sling-Model-Packages> com.sling.models.core.models
</Sling-Model-Packages>
</instructions>
</configuration>
</plugin>
Validate that your class is actually working as a sling model.
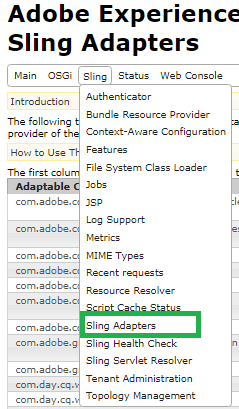
Fig- Sling Adapters in Felix Console
// This model gets the path of the resource . @Model(adaptables = Resource.class)
public class TestModel {
@Inject
Resource resource;
public String getPath() {
return resource.getPath();
}
}
In the initial state of sling models, we used to use @Inject annotation to inject services, pagemanager, sling objects, etc. This is a generic Injector.
Injector Specific Annotations in Sling Model
In AEM Felix console, you can see all the available injectors in sling models 1.3.2
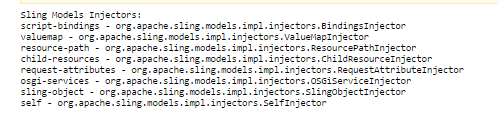
Fig - Injector Specific Annotations in Sling Model
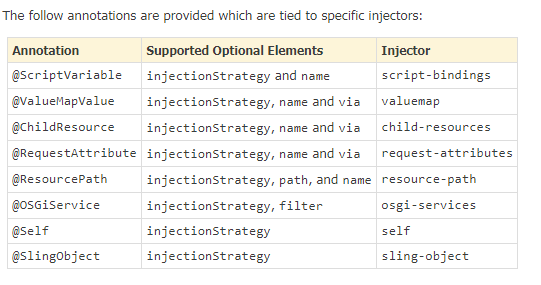
Fig - List of specific injectors
Let’s understand these injectors with the help of examples.
1. Script Variable: This Injector is used to get the currentPage, PageManager, Design, PageProperties, etc. This injector is adaptable to request. This injector is adaptable to SlingHttpServletRequest.
ScriptVariable annotation has these attributes:
public class TestModel {
// Injects currentPage using ScriptVariable annotation
@ScriptVariable(name="currentPage")
Page page;
public String getPagePath() {
return page.getPath();
}
}
</plugin>
Validate that your class is actually working as a sling model.
- Go to Felix Console.
- Click on Sling Adapters from the Sling tab.
Fig- Sling Adapters in Felix Console
- Sling Model class must be visible over here.
// This model gets the path of the resource . @Model(adaptables = Resource.class)
public class TestModel {
@Inject
Resource resource;
public String getPath() {
return resource.getPath();
}
}
In the initial state of sling models, we used to use @Inject annotation to inject services, pagemanager, sling objects, etc. This is a generic Injector.
- @Inject queries all Injector implementations “First Match” wins based on the service ranking.
- Usage of Injector-specific annotations (Introduced in sling models Impl 1.0.6) will reduce the overall work of the internal execution as it specifies the source explicitly so it is good to use Injector specific annotations.
Injector Specific Annotations in Sling Model
In AEM Felix console, you can see all the available injectors in sling models 1.3.2
Fig - Injector Specific Annotations in Sling Model
Fig - List of specific injectors
Let’s understand these injectors with the help of examples.
1. Script Variable: This Injector is used to get the currentPage, PageManager, Design, PageProperties, etc. This injector is adaptable to request. This injector is adaptable to SlingHttpServletRequest.
ScriptVariable annotation has these attributes:
- name
- injectionStrategy: The Strategy can be Optional, Required or Default.
public class TestModel {
// Injects currentPage using ScriptVariable annotation
@ScriptVariable(name="currentPage")
Page page;
public String getPagePath() {
return page.getPath();
}
}
Note: Here it is mandatory to use the object name “currentPage”. If there is a need to change the name of the page object(currentPage), the “name” attribute can help us to do so.
The sightly script to call a sling model is:
<div data-sly-use.example="com.sling.models.core.models.TestModel">
${example.pagePath}<br/>
</div>
2. ChildResource: This injector is adaptable to resource and is used to get the specific child of a resource.
The attributes of the ChildResource are:
- name
- injectionStrategy
- via
@Model(adaptables = Resource.class)
public class TestModel {
// Injects the child of the resource using ChildResource annotation
@ChildResource(name="content")
Resource child;
public String getChildPath() {
return child.getPath();
}
}
Fig - Inject Child resource directly
ChildResource annotations with its attributes:
@Model(adaptables = SlingHttpServletRequest.class)
public class TestModel {
// Injects the child of the resource using ChildResource annotation
@ChildResource(name="content",injectionStrategy= InjectionStrategy.OPTIONAL,via = "resource")
Resource child;
public String getChildPath() {
return child.getPath();
}
}
Note: ChildResource is adaptable to resource, but in the above sample, adaptables is a request. So "via" attribute is used to tell the property that the property is supposed to be fetched via resource.
3.ValueMapValue: This injector is adaptable to the resource. Through this injector, the properties of the resource can be directly injected in the sling models.
The attributes of the ValueMapValue is:
- name
- injectionStrategy
- via
public class TestModel {
// Injects Resource and get ValueMap from the resource
@SlingObject
Resource resource;
public String getTitle() {
ValueMap valueMap = resource.adaptTo(ValueMap.class);
return valueMap.get(“title”, String.class);
}
}
In place of adapting valueMap from the resource and getting the title from valueMap, we can directly use ValueMapValue annotation in sling models.
@Model(adaptables = Resource.class)
public class TestModel {
// Injects title from ValuMapValue
@ValueMapValue
String title;
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
}
Fig - Value Map Sample
The ValueMapValue annotation using its attributes:
@Model(adaptables = SlingHttpServletRequest.class)
public class Test {
// Injects title from ValuMap annotation using its attributes
@ValueMapValue(name = "title",via = "resource",injectionStrategy = InjectionStrategy.REQUIRED)
String pageTitle;
public String getTitle() {
return pageTitle;
}
}
4.ResourcePath: ➤ If a resource is having a property whose value is a path, you can directly use that property as a resource.
➤ You can directly inject a path as a resource using this annotation.
The attributes of the ResourcePath annotation is:
- name
- injectionStrategy
- path
- paths[]
public class TestModel {
//directly inject a path as a resource
@ResourcePath(path = ”/etc/social”)
Resource pathResource;
@ResourcePath(name = "path")
Resource resourcePath;
@ResourcePath(paths = {"/etc/social","/etc/tags"})
Resource[] paths;
}
Fig - Get the Resource bypassing the path dynamically in sling model
5. OSGiService: If we need to inject OSGiService in Sling Models, we can use it like this:
@Model(adaptables = Resource.class)
public class TestModel {
@OSGiService
SlingSettings slingSetttings;
}
6. SlingObject: Supports sling based Objects like request, response, ResourceResolver, Resource, and Sling ScriptHelper.
@Model(adaptables = SlingHttpServletRequest.class)
public class TestModel {
@SlingObject
Resource resource;
@SlingObject
ResourceResolver resourceResolver;
}
7.Self:
➤ Injects the adaptable object itself.
➤ An object that can be adapted from it if the self annotation is present.
The only attribute in the Self annotation is injectionStrategy.
@Model(adaptables = SlingHttpServletRequest.class)
public class SelfExampleModel {
@Self
Node node;
public String getNodePath() throws RepositoryException {
return node.getPath();
}
}
8. Request Attributes: When there are input parameters while initializing the sling model, and you want to get these parameters in the sling model, you can use this annotation.
The attributes of RequestAttribute annotation are:
- name
- injectionStrategy
public class TestModel {
//Injects all the input parameters from sightly injects as RequestAttribute in Sling Models
@RequestAttribute(name = "color")
String param;
public String getParam() {
return param;
}
}
The sightly script calls the sling Model using input parameter :
<div data-sly-use.example="${'com.sling.models.core.models.TestModel ’ @ color='red'}">
${example.param}<br/>
</div>
No comments:
Post a Comment
If you have any doubts or questions, please let us know.