- authentication with OAuth 2.0 (This is for development purposes only. Not a real implementation.)
- querying (using account records)
- inserting (using a contact record related to one of the retrieved account records)
- updating (updates contact record added in previous step)
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
import org.apache.http.Header;
import org.apache.http.HttpResponse;
import org.apache.http.client.HttpClient;
import org.apache.http.client.methods.HttpGet;
import org.apache.http.client.methods.HttpPost;
import org.apache.http.entity.StringEntity;
import org.apache.http.impl.client.DefaultHttpClient;
import org.apache.http.message.BasicHeader;
import org.apache.http.util.EntityUtils;
import org.json.JSONException;
import org.json.JSONObject;
/**
* This program demonstrates the following basic use cases for the REST API:
* - authentication with OAuth 2.0 (This is for development purposes only. Not a real implementation.)
* - querying (using account records)
* - inserting (using a contact record related to one of the retrieved account records)
* - updating (updates contact record added in previous step)
*
*/
public class REST_Code extends Object {
//---------Credentials----------
//Credentials providing access to a specific Salesforce organization.
private static final String userName = "demo@demo.com"; // COPY USERNAME
private static final String password = "passwordTOKEN"; // COPY PASSWORD AND TOKEN
//---------REST and OAuth-------
//Portions of the URI for REST access that are re-used throughout the code
private static String OAUTH_ENDPOINT = "/services/oauth2/token";
private static String REST_ENDPOINT = "/services/data";
//Holds URI returned from OAuth call, which is then used throughout the code.
String baseUri;
//The oauthHeader set in the oauth2Login method, and then added to
//each HTTP object that is used to invoke the REST API.
Header oauthHeader;
//Basic header information added to each HTTP object that is used
//to invoke the REST API.
Header prettyPrintHeader = new BasicHeader("X-PrettyPrint", "1");
//----------Data specific---------
//Retrieved accountId that is used when contact is added.
private static String accountId;
//Id of inserted contact. Used to update contact.
private static String contactId;
//----------Utility-------------
//Used to get input from console.
private static BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
//================Code starts here===================
public static void main(String[] args) {
new REST_Code();
}
/**
* This class holds all the values related to the credentials needed to
* make the OAuth2 request for authentication. Normally they would not be set in
* this manner.
*/
class UserCredentials {
String loginInstanceDomain = "cs10.salesforce.com"; // COPY YOUR SERVER INSTANCE
String apiVersion = "37"; // COPY YOU API VERSION
String userName = REST_Code.userName;
String password = REST_Code.password;
String consumerKey = "CONSUMER_KEY"; // COPY YOUR CONSUMER KEY
String consumerSecret = "CONSUMER_SECRET"; // COPY YOUR CONSUMER SECRET
String grantType = "password";
}
/**
* Constructor drives console interaction and calls appropriate methods.
*/
public REST_Code() {
showMenu();
boolean invalidValue = true;
int executionOption = 99;
String choice = getUserInput("Enter option: ");
while (invalidValue) {
try {
executionOption = Integer.parseInt(choice);
if ((executionOption < 1 || executionOption > 4) && executionOption!=99) {
System.out.println("Please enter 1, 2, 3, 4, or 99.\n");
choice = getUserInput("Enter the number of the sample to run: ");
showMenu();
} else {
invalidValue = false;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Invalid value. Please enter 1, 2, 3, 4, or 99.\n");
choice = getUserInput("Enter the number of the sample to run: ");
showMenu();
}
}
if (executionOption == 99) {
System.out.println("No action taken");
} else {
//Login is done for option 1, as well as all other valid options.
this.oauth2Login();
if (executionOption >= 2) {
this.restGetExample();
}
if (executionOption >= 3) {
if (accountId != null) {
this.restPostExample(accountId);
} else {
System.out.println("Account not found.");
}
}
if (executionOption == 4) {
if (contactId != null) {
this.restPatchExample(contactId);
} else {
System.out.println("Contact not found.");
}
}
}
System.out.println("Program complete.");
}
/**
* This method connects the program to the Salesforce organization using OAuth.
* It stores returned values for further access to organization.
* @param userCredentials Contains all credentials necessary for login
* @return
*/
public HttpResponse oauth2Login() {
System.out.println("_______________ Login _______________");
OAuth2Response oauth2Response = null;
HttpResponse response = null;
UserCredentials userCredentials = new UserCredentials();
String loginHostUri = "https://" + userCredentials.loginInstanceDomain + OAUTH_ENDPOINT;
try {
//Construct the objects for making the request
HttpClient httpClient = new DefaultHttpClient();
HttpPost httpPost = new HttpPost(loginHostUri);
StringBuffer requestBodyText = new StringBuffer("grant_type=password");
requestBodyText.append("&username=");
requestBodyText.append(userCredentials.userName);
requestBodyText.append("&password=");
requestBodyText.append(userCredentials.password);
requestBodyText.append("&client_id=");
requestBodyText.append(userCredentials.consumerKey);
requestBodyText.append("&client_secret=");
requestBodyText.append(userCredentials.consumerSecret);
System.out.println("Response Body: "+requestBodyText.toString());
StringEntity requestBody = new StringEntity(requestBodyText.toString());
requestBody.setContentType("application/x-www-form-urlencoded");
httpPost.setEntity(requestBody);
httpPost.addHeader(prettyPrintHeader);
//Make the request and store the result
response = httpClient.execute(httpPost);
//Parse the result if we were able to connect.
if ( response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode() == 200 ) {
String response_string = EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity());
try {
JSONObject json = new JSONObject(response_string);
oauth2Response = new OAuth2Response(json);
System.out.println("JSON returned by response: +\n" + json.toString(1));
} catch (JSONException je) {
je.printStackTrace();
}
baseUri = oauth2Response.instance_url + REST_ENDPOINT + "/v" + userCredentials.apiVersion +".0";
oauthHeader = new BasicHeader("Authorization", "OAuth " + oauth2Response.access_token);
System.out.println("\nSuccessfully logged in to instance: " + baseUri);
} else {
System.out.println("An error has occured. Http status: " + response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode());
System.out.println(getBody(response.getEntity().getContent()));
System.exit(-1);
}
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException uee) {
uee.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException ioe) {
ioe.printStackTrace();
} catch (NullPointerException npe) {
npe.printStackTrace();
}
return response;
}
/**
* This method demonstrates
* - How to use HTTPGet and a constructed URI to retrieve data from Salesforce.
* - Simple parsing of a JSON object.
*/
public void restGetExample() {
System.out.println("\n_______________ Account QUERY _______________");
try {
//Set up the HTTP objects needed to make the request.
HttpClient httpClient = new DefaultHttpClient();
String uri = baseUri + "/query?q=SELECT+id+,+name+FROM+Account+limit+1";
System.out.println("Query URL: " + uri);
HttpGet httpGet = new HttpGet(uri);
httpGet.addHeader(oauthHeader);
httpGet.addHeader(prettyPrintHeader);
// Make the request.
HttpResponse response = httpClient.execute(httpGet);
// Process the result
int statusCode = response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode();
if (statusCode == 200) {
String response_string = EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity());
try {
JSONObject json = new JSONObject(response_string);
System.out.println("JSON result of Query:\n" + json.toString(1));
accountId = json.getJSONArray("records").getJSONObject(0).getString("Id");
System.out.println("accountId value is " + accountId);
} catch (JSONException je) {
je.printStackTrace();
}
} else {
System.out.println("Query was unsuccessful. Status code returned is " + statusCode);
}
} catch (IOException ioe) {
ioe.printStackTrace();
} catch (NullPointerException npe) {
npe.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* This method demonstrates
* - How to use HTTPPost and a constructed URI to insert data into Salesforce.
* - Simple creation of a JSON object.
*/
public void restPostExample(String accountId) {
System.out.println("\n_______________ Contact INSERT _______________");
String uri = baseUri + "/sobjects/Contact/";
try {
//create the JSON object containing the new contact details.
JSONObject contact = new JSONObject();
contact.put("LastName", "Polsani");
contact.put("FirstName", "Kishore");
contact.put("MobilePhone", "9999999999");
contact.put("Phone", "9999999999");
contact.put("AccountId", accountId);
System.out.println("JSON for contact record to be inserted:\n" + contact.toString(1));
//Construct the objects needed for the request
DefaultHttpClient httpClient = new DefaultHttpClient();
HttpPost httpPost = new HttpPost(uri);
httpPost.addHeader(oauthHeader);
httpPost.addHeader(prettyPrintHeader);
// The message we are going to post
StringEntity body = new StringEntity(contact.toString(1));
body.setContentType("application/json");
httpPost.setEntity(body);
//Make the request
HttpResponse response = httpClient.execute(httpPost);
//Process the results
int statusCode = response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode();
if (statusCode == 201) {
String response_string = EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity());
JSONObject json = new JSONObject(response_string);
// Store the retrieved contact id to use when we update the contact.
contactId = json.getString("id");
System.out.println("New contact id from response: " + contactId);
} else {
System.out.println("Insertion unsuccessful. Status code returned is " + statusCode);
}
} catch (JSONException e) {
System.out.println("Issue creating JSON or processing results");
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException ioe) {
ioe.printStackTrace();
} catch (NullPointerException npe) {
npe.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* This method demonstrates
* - How to use HTTPPatch and a constructed URI to update data in Salesforce.
* NOTE: You have to create the HTTPPatch, as it does not exist in the standard library.
* - Simple creation of a JSON object.
*/
public void restPatchExample(String contactid) {
System.out.println("\n_______________ Contact UPDATE _______________");
//Notice, the id for the record to update is part of the URI, not part of the JSON
String uri = baseUri + "/sobjects/Contact/" + contactid;
try {
//Create the JSON object containing the updated contact phone number
//and the id of the contact we are updating.
JSONObject contact = new JSONObject();
contact.put("Phone", "(415)555-1234");
System.out.println("JSON for update of contact record:\n" + contact.toString(1));
//Set up the objects necessary to make the request.
DefaultHttpClient httpClient = new DefaultHttpClient();
HttpPatch httpPatch = new HttpPatch(uri);
httpPatch.addHeader(oauthHeader);
httpPatch.addHeader(prettyPrintHeader);
StringEntity body = new StringEntity(contact.toString(1));
body.setContentType("application/json");
httpPatch.setEntity(body);
//Make the request
HttpResponse response = httpClient.execute(httpPatch);
//Process the response
int statusCode = response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode();
if (statusCode == 204) {
System.out.println("Updated the contact successfully.");
} else {
System.out.println("Contact update NOT successfully. Status code is " + statusCode);
}
} catch (JSONException e) {
System.out.println("Issue creating JSON or processing results");
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException ioe) {
ioe.printStackTrace();
} catch (NullPointerException npe) {
npe.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* Extend the Apache HttpPost method to implement an HttpPost
* method.
*/
private static class HttpPatch extends HttpPost {
public HttpPatch(String uri) {
super(uri);
}
public String getMethod() {
return "PATCH";
}
}
/**
* This class is used to hold values returned by the OAuth request.
*/
static class OAuth2Response {
String id;
String issued_at;
String instance_url;
String signature;
String access_token;
public OAuth2Response() {
}
public OAuth2Response(JSONObject json) {
try {
id =json.getString("id");
issued_at = json.getString("issued_at");
instance_url = json.getString("instance_url");
signature = json.getString("signature");
access_token = json.getString("access_token");
} catch (JSONException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
//==========utility methods=============
/**
* Utility method for changing a stream into a String.
* @param inputStream
* @return
*/
private String getBody(InputStream inputStream) {
String result = "";
try {
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(inputStream)
);
String inputLine;
while ( (inputLine = in.readLine() ) != null ) {
result += inputLine;
result += "\n";
}
in.close();
} catch (IOException ioe) {
ioe.printStackTrace();
}
return result;
}
//--------------utility methods for user input----------
/**
* A utility method to be used for getting user input from the console.
*/
private String getUserInput(String prompt) {
String result = "";
try {
System.out.print(prompt);
result = reader.readLine();
} catch (IOException ioe) {
ioe.printStackTrace();
}
return result;
}
/**
* Outputs menu choices on console.
*/
private void showMenu() {
System.out.println("");
System.out.println("");
System.out.println(" 1. Login Only");
System.out.println(" 2. Find Account");
System.out.println(" 3. Insert Contact for Account");
System.out.println(" 4. Update Contact");
System.out.println("99. Exit");
System.out.println(" ");
}
} Create an Inbound Integration Using the Force.com REST API
Sample Project
Screenshots:
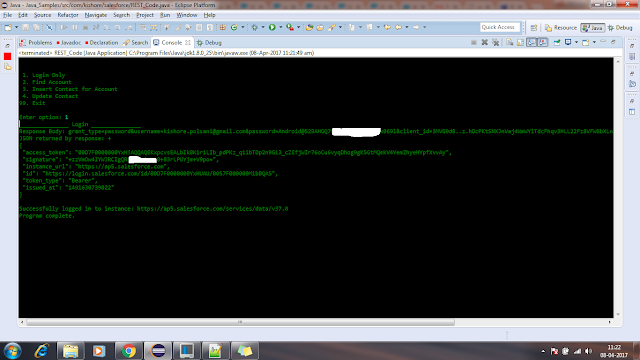
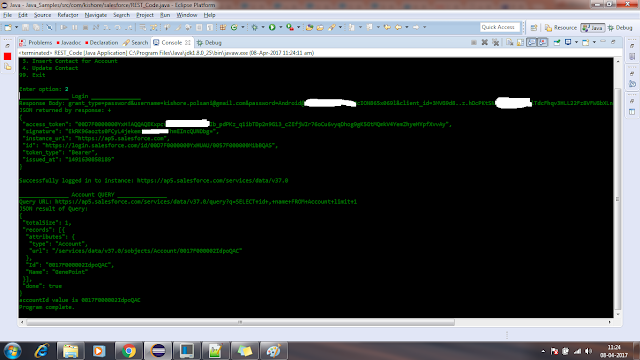
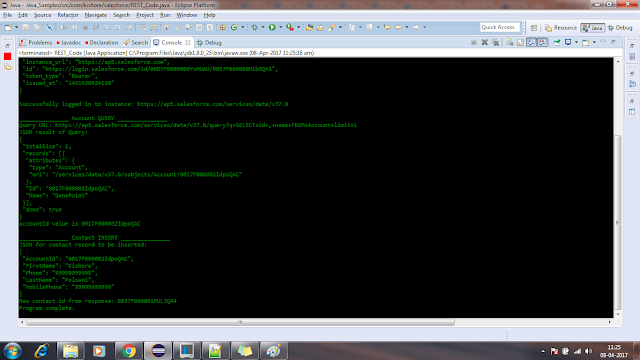
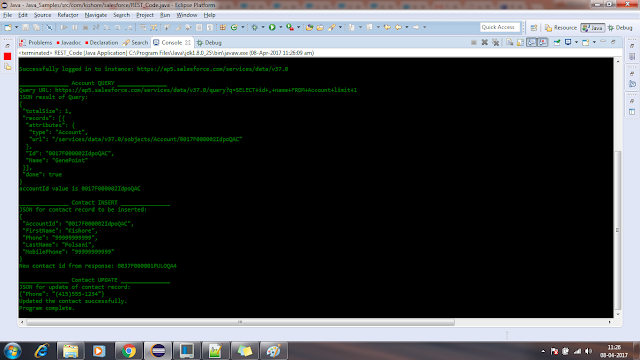
No comments:
Post a Comment
If you have any doubts or questions, please let us know.