Headless CMS in AEM
The headless CMS extension for AEM was introduced with version 6.3 and has been continuously improved since then, it mainly consists of the following components:
The headless CMS extension for AEM was introduced with version 6.3 and has been continuously improved since then, it mainly consists of the following components:
- Content Services: Provides the functionality to expose user-defined content through a HTTP API in JSON format. This allows to deliver data to 3rd party clients other than AEM.
- Content Fragments: Allows the user to insert/edit content as structured data entities. The schema of each content fragment is defined by a corresponding Content Fragment Model.
Example Project
There is a tutorial provided by Adobe where the concept of content services is explained in detail. It describes how to model the entries of a FAQ list by using content fragments, and how to expose this data through a API as JSON. The complete article can be found here.
The example is based on the existing We.Retail demo project that comes with the installation file of AEM. In summary, the following steps have to be performed:
There is a tutorial provided by Adobe where the concept of content services is explained in detail. It describes how to model the entries of a FAQ list by using content fragments, and how to expose this data through a API as JSON. The complete article can be found here.
The example is based on the existing We.Retail demo project that comes with the installation file of AEM. In summary, the following steps have to be performed:
- First content fragment models should be enabled for the We.Retail project. From the AEM welcome page, go to Tools → Configuration Browser, open the properties of the We.Retail configuration and ensure that the Content Fragment Models property has been selected.
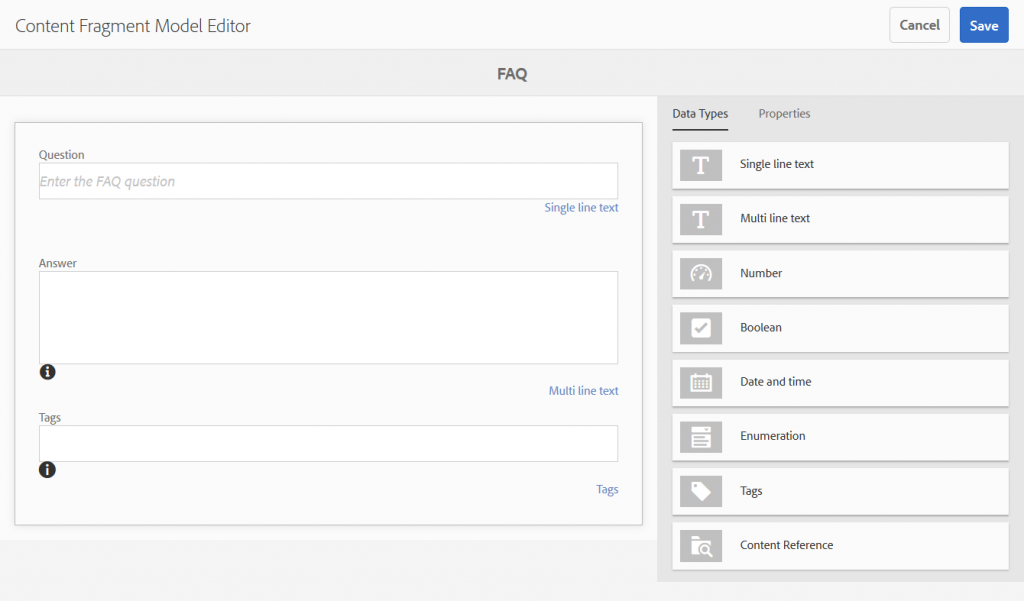
- Navigate to Tools → Assets → Content Fragment Models → We.Retail to create or edit content fragment models. Select the FAQ model and click on the edit button to open the Content Fragment Model Editor. Here you can edit the model structure by adding/removing elements using drag and drop.
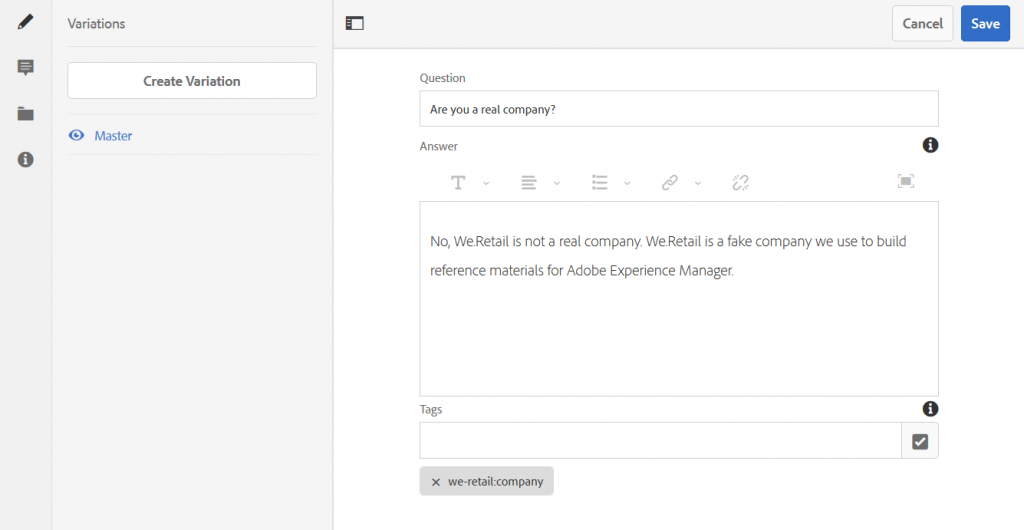
The model can be used to create new content fragments which contain the actual data . To do this, navigate to Assets → Files → We.Retail → English → FAQs → Company. There is already content available here: Each entry of the FAQ list is modeled as a single fragment. The picture below shows the editor view for a FAQ content fragment.
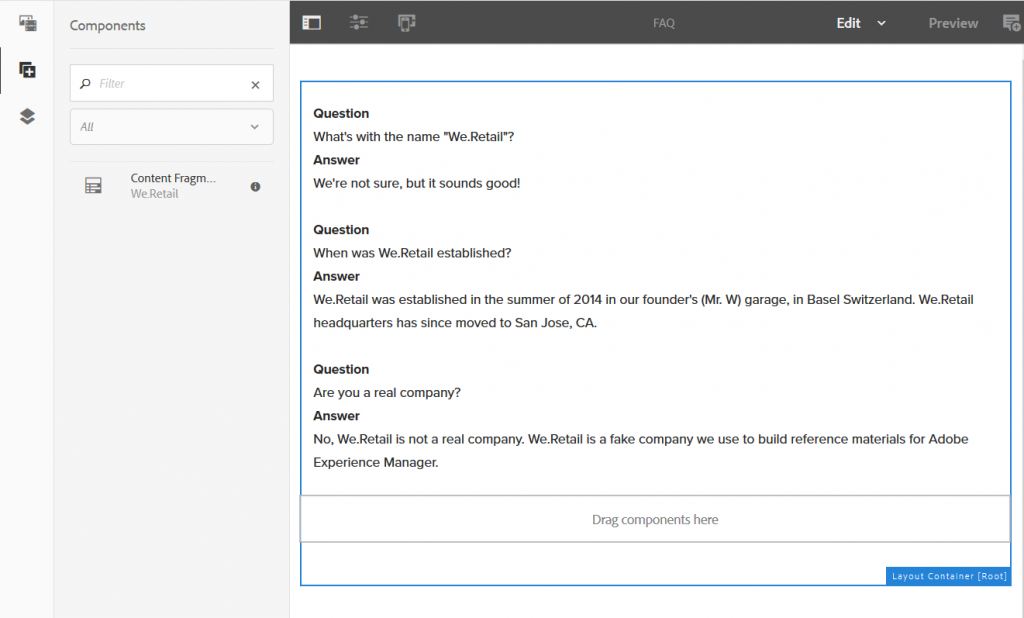
To access the data through content services from outside, the FAQ items have to be embedded within a content page. Content fragments can be added to the page by drag and drop in the same way as any standard content component.
The content of the page can now be delivered as JSON via the “model” selector. The code section below shows an extract of the response of the FAQ page /content/we-retail/language-masters/en/faq.model.json
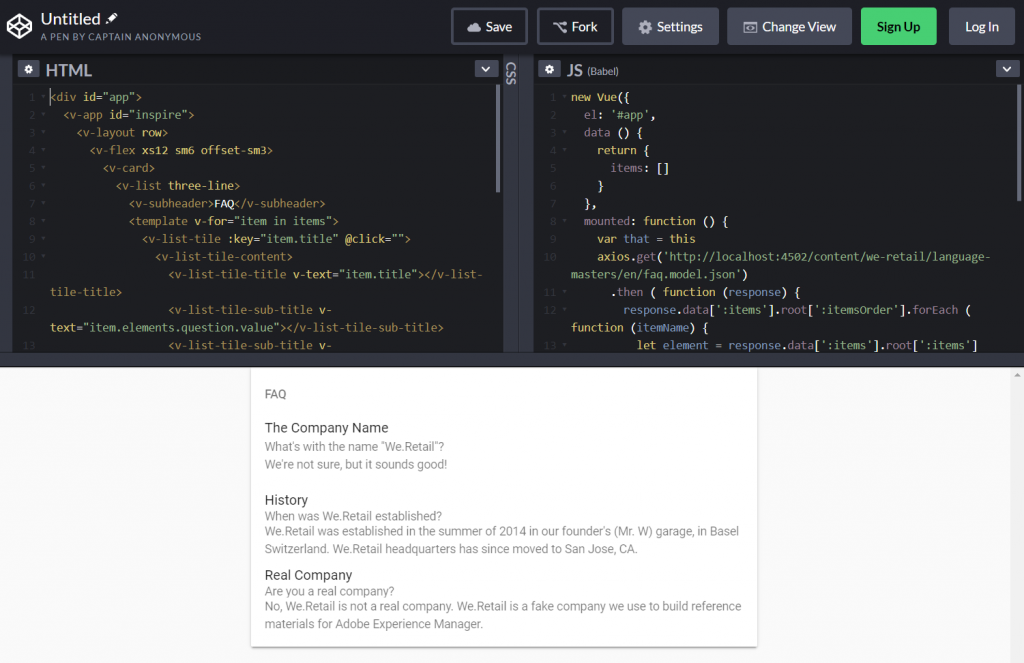
Finally the data can now be consumed by any 3rd party application. The screenshot below shows an example made with vue.js, where the FAQ list is loaded from AEM content services by XHR request.
...
":items": {
"contentfragment": {
"title": "The Company Name",
"description": "",
"model": "we-retail/models/faq",
"elements": {
"question": {
"title": "Question",
"dataType": "string",
"value": "What's with the name \"We.Retail\"?",
":type": "string"
},
"answer": {
"title": "Answer",
"dataType": "string",
"paragraphs": [
""
],
"value": "<p>We're not sure, but it sounds good!<br>\n</p>\n",
":type": "text/html"
}
},
":items": {},
"elementsOrder": [
"question",
"answer"
],
":itemsOrder": [],
":type": "weretail/components/content/contentfragment"
},
"contentfragment_1811741936": {
"title": "History",
...
Finally the data can now be consumed by any 3rd party application. The screenshot below shows an example made with vue.js, where the FAQ list is loaded from AEM content services by XHR request.
Conclusion
AEM content services provide a flexible way to deliver structured content to multiple channels, the data, as well as its corresponding schema, can be created and modified without any need for deployment. However, the main focus of AEM is still on the authoring of backend-side rendered websites, but content services may be a good addition to environments where AEM is already in use.
AEM content services provide a flexible way to deliver structured content to multiple channels, the data, as well as its corresponding schema, can be created and modified without any need for deployment. However, the main focus of AEM is still on the authoring of backend-side rendered websites, but content services may be a good addition to environments where AEM is already in use.
Source: https://www.north-47.com/knowledge-base/exploring-the-headless-cms-functionality-of-aem-6-5/
No comments:
Post a Comment
If you have any doubts or questions, please let us know.