Use the below maven command to create your AEM project and then follow the setup procedure to import in your IDE for further development.
mvn -B archetype:generate \
-D archetypeGroupId=com.adobe.granite.archetypes \
-D archetypeArtifactId=aem-project-archetype \
-D archetypeVersion=23 \
-D aemVersion=cloud \
-D appTitle="My Company" \
-D appId="mycompany" \
-D groupId="com.mycompany" \
-D frontendModule=general \
-D includeExamples=n
Provide frontendModule as react, as we are building a SPA project with react implementation. We will get the corresponding folders applicable to react along with our AEM code folders.

Folder structure after build
Now we can start creating the components in AEM and rendering will be handled by the react end.
React components are placed at ..\ui.frontend\src\components and we have Text OOTB component which is integrated into the AEM component, mapping is done through the MapTo parameter in the JS file.

It is mapped to the Text component of AEM
Similarly, we can create our own react component and Map it to an AEM component and list it in the import-components.js file present inside the components folder in react.
It imports the library to react which enables us to access the Aem component variables in react as props. And this done using the sling model, where we expose these parameters in form JSON using JSON exporter.
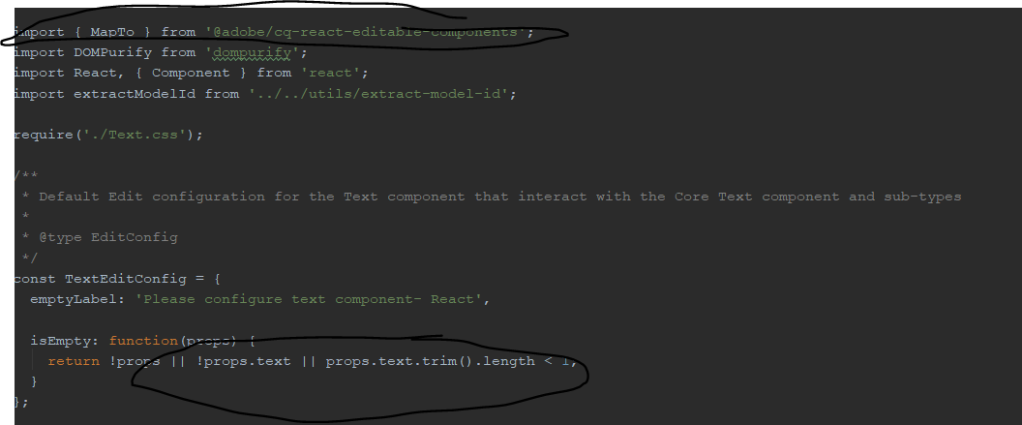
Props fetched and library used
Below is the code snippet that we can use to generate the JSON using the sling model that can be used to provide the props to the react component for rendering.
@Model(adaptables = SlingHttpServletRequest.class, adapters = {
ComponentExporter.class }, resourceType = Title.RESOURCE_TYPE, defaultInjectionStrategy = DefaultInjectionStrategy.OPTIONAL)
@Exporter(name = ExporterConstants.SLING_MODEL_EXPORTER_NAME, extensions = ExporterConstants.SLING_MODEL_EXTENSION)
public class Title implements ComponentExporter {
public static final String RESOURCE_TYPE = "mycompany/components/content/title";
@ValueMapValue
private String title;
@Override
public String getExportedType() {
return RESOURCE_TYPE;
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
}
The important point here is that the language page i.e en.html should be created with the Root template and the child pages should use the content template. The reason being all the JSON gets loaded at the page which we define as the root page.
So, if you open any page under /content/mycompany/us/en it will load us.model.json
And it will have the whole JSON of the site loaded at once.
To verify that you can expand the :children property and can see the JSON of all the child pages under en page.

Try creating some pages under /content/mycompany/us/en and try redirecting between the pages, you will notice that there no page load, and content loads really fast.
NOTE: If your page is not loading then check for the:path variable, as this should match with the URI that you are hitting in the browser. In earlier archetype, we had something called HierarchyPageImpl.java to handle this :path parameter by making changes to the getExportedType function.
Reference: AEM Archetype Adobe
No comments:
Post a Comment
If you have any doubts or questions, please let us know.