THE MINIMUM SET
The Adobe Experience Manager platform requires at least three main actors:
- An author instance for content management.
- A publish instance for delivery of published content to the user.
- A dispatcher on a web server. Technically it is optional but it is vital in order to define caching policies and speed up the navigation on the website.
HOW TO EVALUATE A DEPLOY MODEL
There are several benchmarks to take into account when evaluating qualities and drawbacks of an AEM deploy model. Our comparison will be based on the following properties:
- Fault tolerance: how robust we want to be with respect to downtimes;
- Editor performances: speed up content creation and management;
- End-user performances: provide the best possible site navigation experience;
- Scalability: how our infrastructure is able to face traffic peeks;
- Content management: how much space is required to manage all the required contents.
In most scenarios the first requirement we need to satisfy is fault tolerance, above all at the publish layer.
Based on this assumption we will not evaluate models without at least 2 or more publish instances.
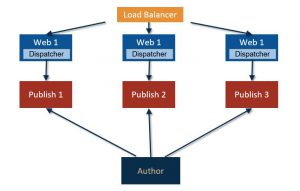
This is the most basic and efficient setup:
- One author: since we are not setting up a cluster we are accepting a potential downtime.
- Two or more publish servers (based on your needs) onto which the author replicates all contents.
- A dedicated dispatcher for each publish.
- A load balancer to distribute traffic on all the chains.
On the other hand, there is no fault tolerance on the author instance and it is required a DataStore for each instance which, in certain scenarios, means a lot of disk space to provide.
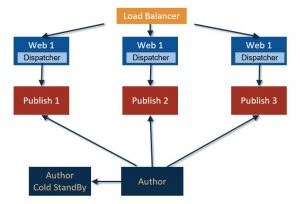
The first optimization you can think about is to provide fault tolerance for the author instance adding a cold stand-by server next to the author one. This solution is not a “so quick recovery solution”, since the instance has to reconfigured and restarted when needed. It is a ready to use copy of the author and costs less than an actual working author instance. An eventual downtime is not avoided but potentially reduced.
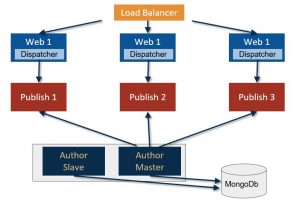
This model achieves the actual fault tolerance for author instances. The two author instances are both up and running and in case of unavailability of one of them the other will continue to deliver the authoring service.
This redundancy provides no downtime for the editor. In order to be always aligned, these two instances will share the NodeStore through a MongoDB database. MongoDB can be configured in different ways and normally will provide fault tolerance itself with different replica sets and an arbiter.
DEPLOY MODEL N.4 – SHARED DATASTORE
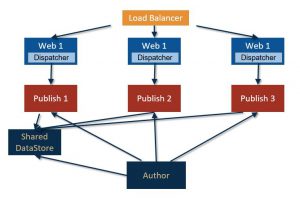
AEM Deployment Model 4
This enhancement targets disk space optimization. Sharing the DataStore allows to save up a great amount of space. Assets are not saved and replicated anymore on each server but are available on a common server.
This solution helps also the publishing experience of the editor since binaries of the assets do not have to be replicated from author to publish nodes. Content activation time is greatly reduced.
In the image is shown the DataStore shared between all publish and the author instance: technically there is also the option to share it only across publish instances. This choice helps content separation between published and not published assets but loses the replication time improvements and part of the disk space savings.
This solution helps also the publishing experience of the editor since binaries of the assets do not have to be replicated from author to publish nodes. Content activation time is greatly reduced.
In the image is shown the DataStore shared between all publish and the author instance: technically there is also the option to share it only across publish instances. This choice helps content separation between published and not published assets but loses the replication time improvements and part of the disk space savings.
DEPLOY MODEL N.5 – AMAZON S3
With AEM is also possible to configure the DataStore on a cloud server provided by Amazon. This solution is applicable to the shared DataStore model and amplifies the advantages of that deploy.
Amazon provides nearly unlimited storage and at a cheaper storage cost. There is no replication of contents and the client is guaranteed some data recovery solution (disk redundancy and backups are not part of this post).
A possible drawback regards times in delivering contents to the publish instances (and consequentially to the end users). This configuration does not work anymore on an intranet but on a cloud internet service.
With AEM is also possible to configure the DataStore on a cloud server provided by Amazon. This solution is applicable to the shared DataStore model and amplifies the advantages of that deploy.
Amazon provides nearly unlimited storage and at a cheaper storage cost. There is no replication of contents and the client is guaranteed some data recovery solution (disk redundancy and backups are not part of this post).
A possible drawback regards times in delivering contents to the publish instances (and consequentially to the end users). This configuration does not work anymore on an intranet but on a cloud internet service.
CONSIDERATIONS
Five shown approaches are only a quick overview of deploy models that can be used in a AEM project.
The focus was on deploy topologies rather than on ways to handle storage of the NodeStore (for instance: TarMK vs MongoDB) or of the DataStore (FileSystem vs MongoDB vs AmazonS3), but also these topics are going to have big impacts on performances.
All approaches have their strengths and there is not a perfect model usable in every project. You need also to consider that each of these models requires different budgets.
In order to achieve the best solution, it is important to focus on main requirements of the stakeholder and understand what should be guaranteed and what eventually can be temporarily compromised.
Five shown approaches are only a quick overview of deploy models that can be used in a AEM project.
The focus was on deploy topologies rather than on ways to handle storage of the NodeStore (for instance: TarMK vs MongoDB) or of the DataStore (FileSystem vs MongoDB vs AmazonS3), but also these topics are going to have big impacts on performances.
All approaches have their strengths and there is not a perfect model usable in every project. You need also to consider that each of these models requires different budgets.
In order to achieve the best solution, it is important to focus on main requirements of the stakeholder and understand what should be guaranteed and what eventually can be temporarily compromised.
AUTHORS
Fernando Diaz Martin, Marco Pasini
Fernando Diaz Martin, Marco Pasini
BIBLIOGRAPHY
https://docs.adobe.com/docs/en/aem/6-2/deploy/recommended-deploys.html
http://ashokkumarta.blogspot.it/2015/11/mongo-vs-tar-mk-big-debate.html
http://www.weishao.me/blog/using-amazon-s3-as-the-datastore-in-adobe-aem
https://docs.adobe.com/docs/en/aem/6-2/deploy/recommended-deploys.html
http://ashokkumarta.blogspot.it/2015/11/mongo-vs-tar-mk-big-debate.html
http://www.weishao.me/blog/using-amazon-s3-as-the-datastore-in-adobe-aem
No comments:
Post a Comment
If you have any doubts or questions, please let us know.